Xss Basics
Input Validation Attacks
Attacks triggered by user input are called input validation attacks. Malicious input can successfully subvert the funtioning an application because of either insufficient validation by the application or by the server before using the data.\
Most web application vulnerabilities are the result of poor coding design and ignorance on best practicies in secure coding methodologies.\
Samle of some input validations attacks are : XSS, SQL Injections, HTTP header tampering and many others.
XSS
Cross site scripting is an attack in which its ultimate purpose is to inject HTML or run javascript code in a user’s Web browser.
Sample Vulnerable Code
<?php
echo '<h4> Hello ' . $_GET['name'] . '</h4>';
?>
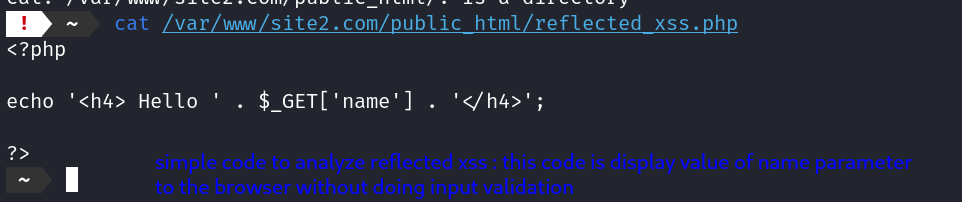
The above code prints a welcome message to the user whose name is retrived from the $_GET variable.
User input : http://site2.com/reflected_xss.php?name=Numan
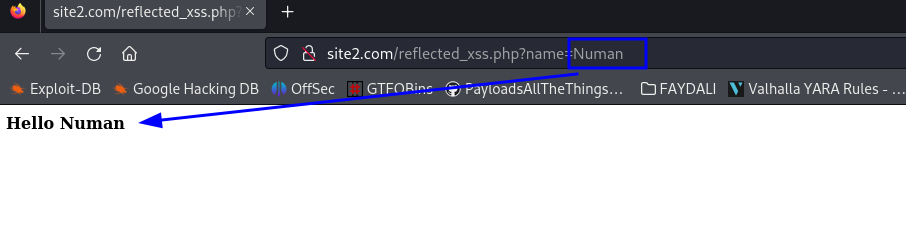
Note : ?name=Numan is called querystring
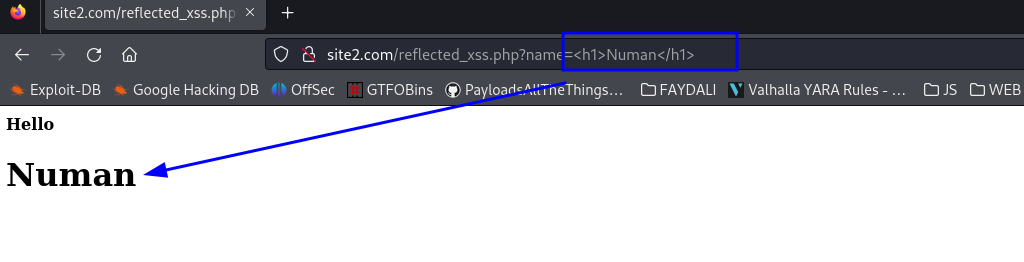
Lets see what if an attacker send html value to the parameter ?
Attacker html input : http://site2.com/reflected_xss.php?name=<h1>Numan</h1>
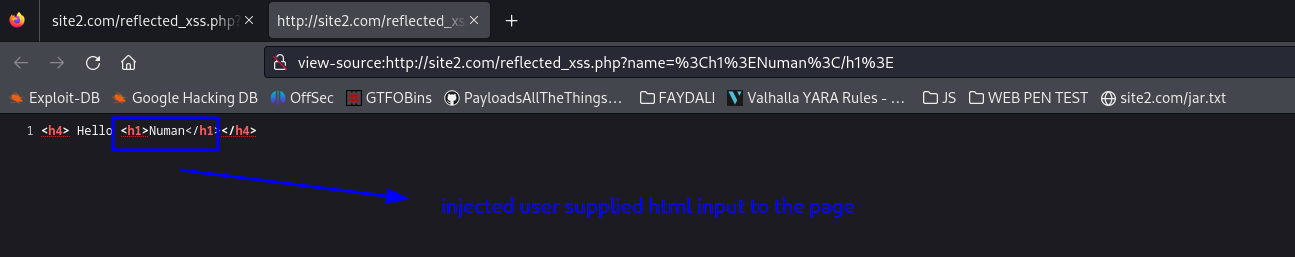
Analyse source page of the web page and see we can inject html codes succesfully to the web page
Lets one step further and analyze what if we can supplied javascript code to the querystring’s parameter
Attacker input : http://site2.com/reflected_xss.php?name=<script>alert(“XSS”)</script>
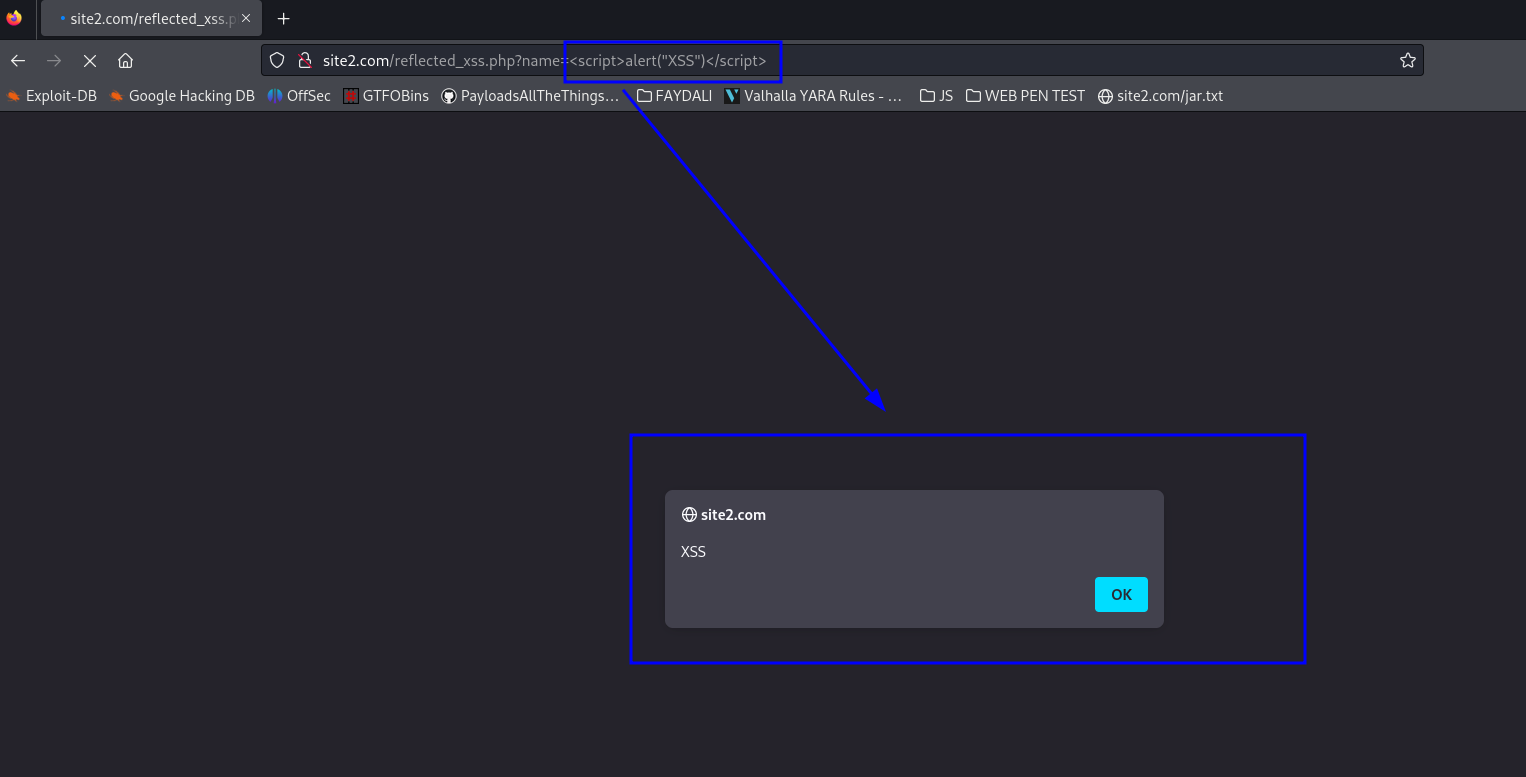
We can successfully execute js code in the web page. When we analyze the source code of the web page we can see the js code which we sullied.
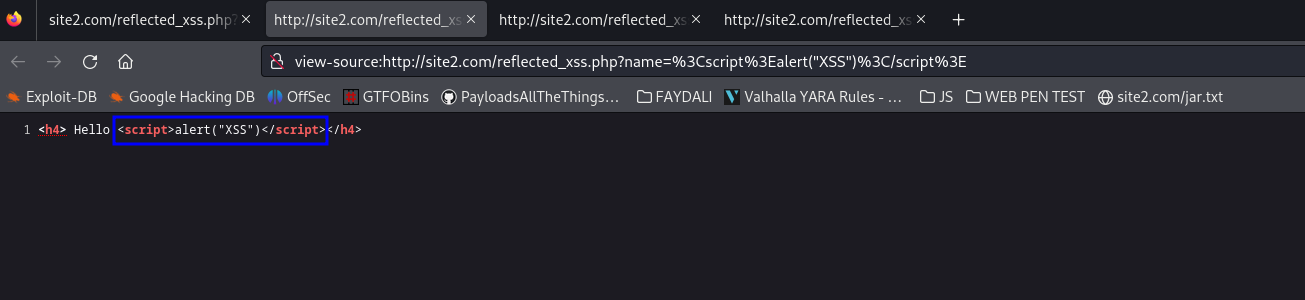
Why does this happen ?
Because the user input is given on output without any kind of sanitization (either on input or output.)
Cross site scripting attacks are possible when the user input is used somewhere on the web application output; this lets an attacker get control over the content rendered to the application users thus attacking the user themselves.
We can prevent xss attack using with input sanitazion and output escaping
<?php
$name = isset($_GET['name']) ? $_GET['name'] : 'Guest';
// Input validation: Allow only alphanumeric characters and spaces
if (preg_match('/^[A-Za-z0-9\s]+$/', $name)) {
// Output escaping using htmlspecialchars
$name = htmlspecialchars($name, ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8');
echo "<h4> Hello $name </h4>";
} else {
echo "<h4> Hello Guest </h4>";
}
?>
In this code :
- We first set the ‘name’ variable to the value from the ‘name’ parameter if it exists, or to “Guest” if it doesn’t.
- We use a regular expression (preg_match) to check whether ‘name’ contains only alphanumeric characters and spaces.
- If the input passes the validation, we use htmlspecialchars to escape the ‘name’ variable before echoing it. This ensures that any potentially harmful characters in the ‘name’ parameter are properly converted to HTML entities, preventing XSS attacks.
- If the input doesn’t meet the validation criteria, it defaults to “Guest.”
By combining input validation and output escaping, you have a secure PHP code snippet that both validates and safely displays the ‘name’ parameter.